Permalink: https://msnstudy.com/picot-questions/
PICOT Questions Examples
Whether they’re finishing advanced studies in nursing school or working in a professional clinical setting, registered nurses (RNs) begin their research queries using an evidence-based practice framework developed from a well-constructed PICOT question.
The word PICOT is a mnemonic derived from the elements of a clinical research question – patient, intervention, comparison, outcome and (sometimes) time. The PICOT process begins with a case scenario, and the question is phrased to elicit an answer.
“The question needs to identify the patient or population we intend to study, the intervention or treatment we plan to use, the comparison of one intervention to another (if applicable) and the outcome we anticipate,” Kathy A. Jensen, MHA, RN, wrote in EBSCO Health’s whitepaper, “7 Steps To The Perfect Pico Search.” “Once a well-structured question is formulated, researchers will be in a better position to search the literature for evidence that will support their original PICO question.”
This his blog post discusses PICOT Questions with some elaborative examples. As you continue, premiumacademicaffiliates.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order with us.
Learning the PICOT Process
The PICOT process generally begins with a vague clinical query. Each element of the process helps develop a well-structured question. Once established, researchers can search for evidence that will help answer the inquiry.
As you continue premiumacademicaffiliates.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order with us.

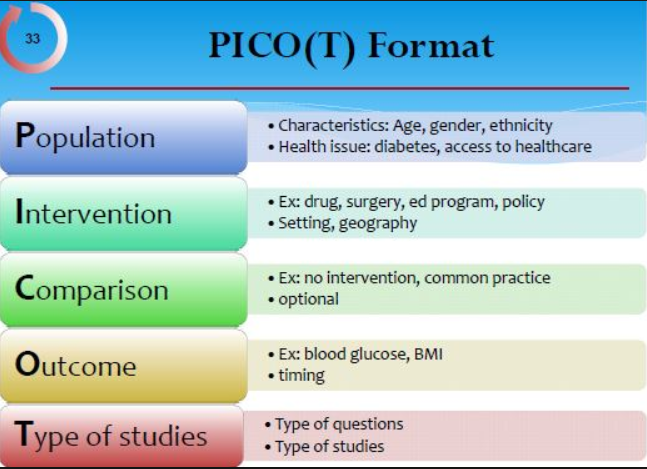
The elements of a PICOT question are:
P (Patient, population or problem)
Who or what is the patient, population or problem in question?
I (Intervention)
What is the intervention (action or treatment) being considered?
C (Comparison or control)
What other interventions should be considered?
O (Outcome or objective)
What is the desired or expected outcome or objective?
T (Time frame)
How long will it take to reach the desired outcome?
Using the PICOT process helps develop a careful and thoughtful question that makes the search for evidence easier, the University of Oxford’s world-renowned Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine said.
“The well-formed question makes it relatively straightforward to elicit and combine the appropriate terms needed to represent your need for information in the query language of whichever searching service is available to you,” the University of Oxford author said. “Once you have formed the question using the PICO structure, you can think about what type of question it is you are asking, and therefore what type of research would provide the best answer.”
Steps to the PICOT Process
In developing a PICOT question, researchers must identify a need or a reason for the study. In the EBSCO Health whitepaper, the general example used is this: A committee decides to conduct a case study to determine whether postoperative gum chewing for abdominal surgery patients can prevent postoperative ileus (lack of intestinal movement).
With the scenario in mind, researchers use seven steps to the PICOT search:
- Formulate the PICOT question in general terms: Based on the EBSCO Health example, the research question would be, “In patients recovering from abdominal surgery, is there evidence that suggests gum-chewing postoperatively, compared to not chewing gum, impacts postoperative ileus?”
- Identify the keywords for the PICOT mnemonic: P – Patients recovering from abdominal surgery I – Gum chewing C – Not chewing gum O – Impacts post-operative ileus
- Plan the search strategy: With the question in mind, researchers consider which databases and other search sites they might use to find information and answers. Researchers use strategies to maximize their search terms such as looking up synonyms and phrases that mean the same thing.
- Execute a search: At first, researchers search each PICOT element individually. For example, when researching patients recovering from abdominal surgery, use the search terms “abdominal surgery,” but also consider the search terms “recovery and postoperative.”
- Refine the results: Narrow the search results by limiting the works to pertinent content, such as articles from peer-reviewed journals or research documents.
- Review the content: Review the research results to establish if they have the necessary information to answer the PICOT question.
- Determine if research results meet standards: After reviewing the research results, determine whether they provide the best available evidence.
After the PICOT question is constructed and researched, the information garnered is used to determine which type of study is most appropriate. Study types include meta-analysis, systematic review, randomized controlled trial, cohort study, case-control study and case report.
“The actual search for high-quality clinical research evidence can be overwhelming to many,” Jensen said in the EBSCO Health whitepaper. “By utilizing the PICO format, the search process will be streamlined and will yield the best available evidence to support clinical decisions and explore alternative treatments and procedures.”
DNP and PICOT Question
To take a deep dive into advanced nursing practice, many RNs seeking a DNP must submit a final project.
Through the project, DNP candidates will identify a specific problem in patient care or clinical practice and present solutions. Students use a PICOT question to guide the project topic.
The online DNP program teaches RNs nurse manager competencies as well as other essential leadership skills. The university offers three distinct DNP tracks:
- Clinical Leadership DNP
- Post-Bachelor’s Executive Nurse Leadership DNP
- Post-Master’s Executive Nurse Leadership DNP
As you continue premiumacademicaffiliates.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order with us.

Evidence-Based PICOT Questions Examples
- PICOT Questions:
Population: Bariatric adolescents considering or undergoing gastric bypass surgery.
Intervention: The nurse’s role as a primary member of the multidisciplinary team regarding perioperative care of the bariatric adolescent patient.
Comparison: The nurse’s role as a secondary member of the multidisciplinary team without any specialized training and is only involved in perioperative care of the bariatric adolescent patient.
Outcome: When the nurse is involved as one of the primary members in the multidisciplinary team approach, the bariatric adolescent patient has better continuity of care.
Time: perioperative including the 6 weeks post recovery.
PICOT Question: Does the bariatric adolescent patient undergoing gastric bypass have better continuity of care perioperatively and postoperatively when the nurse is a primary member of the multidisciplinary team versus when the nurse is a secondary member whose only role is in providing perioperative care and has no specialized training?
- Intervention PICOT Question Examples, an Intervention example:
In adult patients with total hip replacements (Patient population) how effective is PCA pain medication (Intervention of interest) compared to prn IM pain medication (Comparison intervention) in controlling post operative pain (Outcome) during the perioperative and recovery time? Note: The IM pain medication would be called the control group. It would be unethical to have a control group that received NO pain medication. Many times the control group means they get “business as usual!” or the current standard of care.
- Therapy PICOT Question Examples, a non-intervention example:
What is the duration of recovery (O) for patients with total hip replacement (P) who developed a post-operative infection (I) as opposed to those who did not (C) within the first six weeks of recovery (T)?
- Etiology PICOT Question Examples:
Are kids (P) who have obese adoptive parents (I) at Increased risk for obesity (O) compared with kids (P) without obese adoptive parents (C) during the ages of five and 18 (T)?
- Diagnostic PICOT Question Examples:
Is a PKU test (I) done on two week old infants (P) more accurate in diagnosis inborn errors in metabolism (O) compared with PKU tests done at 24 hours of age (C)? Time is implied in two weeks and 24 hours old.
- Prevention PICOT Question Examples:
In OR nurses doing a five minute scrub (P) what are the differences in the presence and types of microbes (O) found on natural polished nails and nail beds (I) and artificial nails (C) at the time of surgery (T)?
- Prognosis/Prediction PICOT Question Examples:
Does telelmonitoring blood pressure (I) in urban African Americans with hypertension (P) improve blood pressure control (O) within the six months of initiation of the medication (T)?
- Meaning PPICOT Question Examples:
How do pregnant women (P) newly diagnosed with diabetes (I) perceive reporting their blood sugar levels (O) to their healthcare providers during their pregnancy and six weeks postpartum (T)?
PICOT Questions Examples
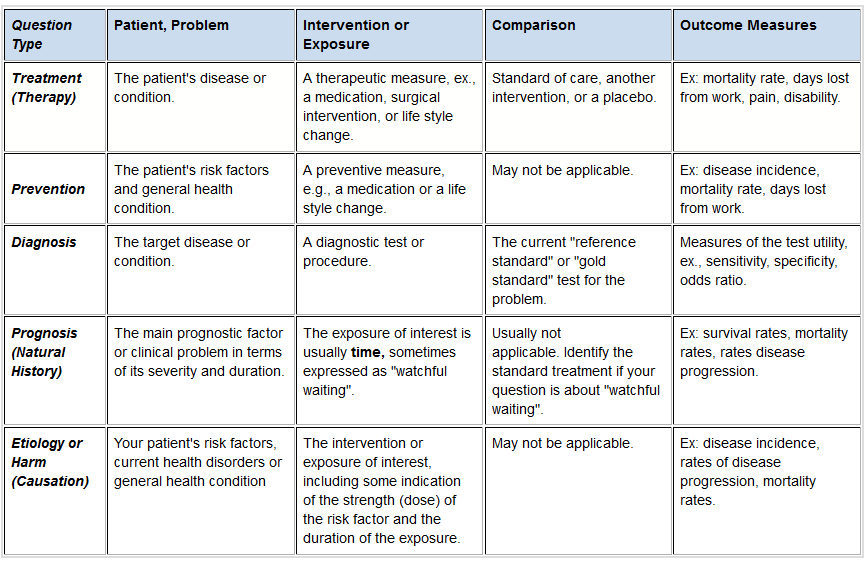
| Element of the clinical question | Population/Patient/Problem Describe as accurately as possible the patient or group of patients of interest. | Intervention (or cause, prognosis) What is the main intervention or therapy you wish to consider? Including an exposure to disease, a diagnostic test, a prognostic factor, a treatment, a patient perception, a risk factor, etc. | Comparison (optional) Is there an alternative treatment to compare? Including no disease, placebo, a different prognostic factor, absence of risk factor, etc. | Outcome What is the clinical outcome, including a time horizon if relevant? |
| Example | In patients with acute bronchitis, | do antibiotics | none | reduce sputum production, cough or days off? |
| Example | In children with cancer | what are the current treatments | in the management of fever and infection? | |
| Example | Among family-members of patients undergoing diagnostic procedures | does standard care, | listening to tranquil music, or audio taped comedy routines | make a difference in the reduction of reported anxiety. |
As you continue premiumacademicaffiliates.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order with us.

Asking Different Types of Questions
Practice Your Skills
Practice writing out PICO components and then forming a focused questions below.
Information and samples borrowed from UNC-CH HSL.
1. Cardiology
Scenario:
Patients on coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) waiting lists often experience anxiety and depression and your nurse manager wants to know if it would be a good idea to reach out to these patients with presurgical home visits and follow-up calls from a specialist cardiac nurse.
P: patients on CABG waiting lists I: program consisting of presurgical home visit and follow-up calls form a specialist cardiac nurse C: no intervention O: decreased patient anxiety and depression
For patients on CABG waiting lists, does an intervention program consisting of presurgical home visits and follow-up calls from a specialist cardiac nurse lead to decreased patient anxiety and depression [when compared with no intervention]?
2. ICU
Scenario:
You work in the Big City Hospital ICU. Your mechanically ventilated patients sometimes contract nosocomial pneumonia, which leads to costly complications. You want to know if raising the head of the bed lowers the chance of the patient contracting pneumonia compared to letting the patient lie flat on their back.
P: mechanically ventilated ICU patients I: semi-fowlers position C: supine position O: lower incidence of nosocomial pneumonia In mechanically ventilated ICU patients, does positioning the patient in semi-fowlers result in a lower incidence of nosocomial pneumonia when compared to the supine position?
3. Infection Control
Scenario:
In the past few years, your hospital has installed antibacterial foam dispensers on all the nursing units. You’ve had nurses asking you if the foam is just as effective as washing their hands with water and soap.
P: hospital nurses I: using antibacterial foam C: hand washing with soap and water O: decreased bacteria count In hospital nurses, does antibacterial foam decrease bacteria count on hands as much as hand washing with soap and water?
4. Labor & Delivery
Scenario:
You’re a new nurse on a labor and delivery unit. You’ve noticed that most women give birth in the lithotomy position at the encouragement of their doctors. However, you’re sure you heard in nursing school that other positions are less likely to lead to deliveries with forceps or a vacuum.. or did you? You want to find some literature to back up your claim.
P: laboring women delivering in a hospital I: positions other than the lithotomy position C: lithotomy position O: decreased incidence of assisted deliveries In laboring women delivering in the hospital, do positions other than lithotomy position lead to a decreased incidence of assisted deliveries?
As you continue premiumacademicaffiliates.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order with us.

5. NICO
Scenario:
You’re the nurse manager of a NICU unit. One concern of parents of infants receiving tube feedings is being able to successfully breastfeed their child upon discharge. One of your staff nurses asks if it would be helpful to give the infants cup feedings instead of tube feedings during their NICU stay.
P: Infants in the NICU I: cup feeding throughout the hospital stay C: tube feedings throughout the hospital stay O: greater reported success with breastfeeding post-discharge In infants in the NICU, will cup feeding throughout the hospital stay lead to greater success with breastfeeding post-discharge when compared to tube feedings?
6. Oncology
Scenario:
You work with patients with advanced cancer and have been taught to suggest pain diaries for your patients as a form of pain management. You’ve been wondering for a while now if these diaries actually improve pain control or make pain worse by making patients more aware of their pain.
P: patients with advanced cancer I: keeping a pain journal C: no intervention O: lower reported pain scores In patients with advanced cancer, does keeping a pain journal result in lower reported pain scores when compared to no intervention?
7. Pediatrics
Scenario:
You work in a pediatrician’s office and give patients their routine vaccinations. The younger children are often fearful of needles, and some of the RNs use toys to distract the patients. You want to know if this technique actually has an effect on the children’s pain response.
P: young children I: distraction techniques during immunization C: no intervention O: lower pain scores rated by the Faces pain scale In young children, do distraction techniques during immunization administration using toys result in lower pain scores when compared to no intervention?
8. Psychiatry
Scenario:
You work on an inpatient psychiatric unit. One of your patients with chronic schizophrenia, Joe, normally mumbles to himself, but will occasionally speak to others when residents play games together. Noticing this, you say to a coworker that maybe social skills group training sessions would bring out Joe’s conversational skills. Your coworker shakes her head and says “I don’t think so. Joe is in and out of this hospital, he’s a lost cause.”
P: Inpatient chronic schizophrenia patients I: social skills group training sessions C: standard care O: increased conversational skills as evidenced by greater number of interactions with peers In inpatient chronic schizophrenia patients, do social skills group training sessions increase conversational skills when compared to standard care?
9. Wound Care
Scenario:
A diabetic patient from a nursing home has recently been admitted with a stage III pressure ulcers on his heels. The unit nurses have called you in for a wound consult. You have to choose between standard moist wound therapy and using a wound vac.
P: elderly diabetic with stage III foot ulcers I: negative pressure wound therapy C: standard moist wound therapy O: improved wound healing as measured by pressure ulcer grading system guidelines In elderly diabetic patients with stage III foot ulcers, does negative pressure wound therapy lead to improved wound healing when compared to standard moist wound therapy?
10. PACU
Scenario:
The main concern for most of your patients coming out of anesthesia in your PACU is pain. You want to explore nursing interventions you can use on top of medication administration to decrease pain. One coworker mentions trying to make the PACU feel less clinical by playing soft music to relax patients.
P: PACU patients I: soft music as an adjunct to standard care C: standard care alone O: lower reported pain scores In PACU patients, will playing soft music in the PACU as an adjunct to standard care result in lower reported pain scores when compared to standard care alone?
Sources
EBSCO Health, “7 Steps to The Perfect Pico Search” University of Oxford, “Asking Focused Questions”
